Hepatitis and Liver Cancer
- When the liver cells grow out of control, liver cancer can be developed. The most common type of liver cancer in Hong Kong is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- In Hong Kong, the majority of liver cancer cases are related to hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
- Local studies showed that 75 - 80% of HCC cases were related to chronic HBV infection, and 3 - 6% of the cases were related to chronic HCV infection. HBV and HCV co-infection accounted for another 0.4 - 3%.
- Other risk factors of liver cancer include cirrhosis, excessive consumption of alcohol, eating foods contaminated with aflatoxin (e.g. mouldy grains and peanuts), diabetes, obesity and smoking.
- Some people fail to clear the virus may develop chronic hepatitis, which may develop cirrhosis and liver cancer.
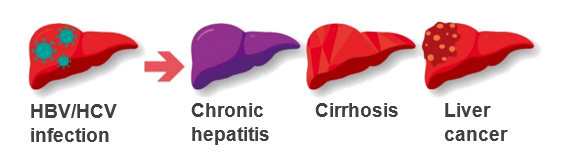
- HBV and HCV infection can remain asymptomatic until decades after infection, and when signs and symptoms, such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin and the whites of eyes) and tea-coloured urine, develop secondary to serious liver damage.
How people with chronic hepatitis reduce their risk of liver cancer?
Regular check-ups
- People with chronic HBV infection, chronic HCV infection or cirrhosis are at increased risk of liver cancer.
- Depending on certain criteria such as age, family history, presence of cirrhosis and other clinical parameters, some subgroups are at higher risk and should consider receiving periodic cancer surveillance (e.g. every 6 -12 months) with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test and ultrasonography.
- People with chronic HBV infection, HCV infection or cirrhosis should seek advice from doctors to determine their need for and approach of cancer surveillance.
Antiviral Treatment
- Antiviral treatment can suppress viral replication and improve the liver condition of people with HBV infection, thereby reducing the risk of cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer. It should be noted that not every person with chronic hepatitis needs antiviral treatment. Doctors will conduct thorough assessment to determine an appropriate management plan.
- People with HCV infection should receive curative treatment with direct-acting antivirals (DAA). With successful clearance of HCV, the risk of progression to cirrhosis, liver cancer and dying from liver diseases can be significantly reduced.
Maintain healthy diet and lifestyle
- Do not smoke and drink
- Maintain balanced diet with abundant fresh vegetables and fruits
- Avoid eating raw or undercooked shellfish
- Do not take medication with uncertain ingredients to avoid liver damage
- Be physically active and maintain healthy body weight
HBV and HCV infection can be prevented and treated
Please click the links below for more information: