Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Hepatitis B vaccine is effective in preventing hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
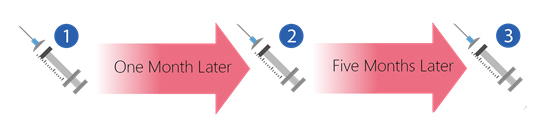
- The complete course of vaccination takes a total of three doses. The second dose is given 1 month after the first, and the third dose is given 5 months after the second.
- If there is an interruption between doses of hepatitis B vaccine, it is not necessary to re-start the vaccine series. Arrangement for the subsequent doses should be made as soon as possible.
- After completion of the three-dose course of hepatitis B vaccination, more than 95% of healthy people would produce protective antibody levels, which can confer long-term protection against HBV infection.
- Hepatitis B vaccine is very safe and its side effects are minimal. Occasionally there may be slight soreness around the injection site and it usually resolves within one to two days after vaccination.
- Anyone, who is allergic to any component in hepatitis B vaccine (e.g. yeast) or has ever had allergic reaction after the previous dose of hepatitis B vaccine, should not receive the vaccine
Universal childhood hepatitis B vaccination programme
- In endemic places, most persons with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) acquired HBV infection by mother-to-child transmission (MTCT). Hepatitis B vaccination is an important measure in preventing MTCT.
- Since 1988, the universal childhood hepatitis B vaccination programme has been implemented in Hong Kong, greatly reducing the risk of HBV infection.
- All babies born in Hong Kong receive the birth dose of vaccination in hospital. The second and third doses are given at 1 month and 6 months of age.
- Maternal and Child Health Centres of the Department of Health (DH) offer hepatitis B vaccination to children from birth to five years old. Please click here for the vaccination procedure.
- For primary school children who have not completed hepatitis B vaccination, the School Immunisation Teams under the Centre for Health Protection of DH provide mop-up vaccination services.
Persons at higher risk of infection should consider receiving hepatitis B vaccine
- The following groups considered at higher risk of HBV infection should receive hepatitis B vaccine, for example:
- Family members (such as parents, siblings and offspring) and sexual partners of people with CHB
- People who inject drugs (PWID)
- Men who have sex with men
- People with multiple sexual partners
- HIV-positive people
- People who receive blood or blood products on regular basis
- People on dialysis
- Healthcare workers who may have occupational exposure to blood or other body fluids of patients
- For adults, it is preferable to have blood tests for hepatitis B status before vaccination.
- Vaccination is not required for people who already have protective antibody for HBV
- If you are tested to be infected with HBV, vaccination will not be effective. You should consult a doctor for assessment and treatment of HBV infection.
- Only persons without HBV infection and protective antibody require hepatitis B vaccination.
- For details about hepatitis B, please click here.
- Please consult your family doctor if you want to receive hepatitis B vaccination. You may refer to the Primary Care Directory to find a suitable family doctor.
Health Education Materials
Useful link